F-35:
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a family of fifth-generation, single-seat, single-engine stealth multirole fighters. After entering service it would be considered as the most advanced fighter aircraft in the world, performing ground attack, reconnaissance, and air defense missions.The F-35 Lightning II, also known as the Joint Strike Fighter (JSF), integrates advanced very low observable stealth into a supersonic, highly agile 5th generation fighter. The capabilities built into the F-35 Lightning II provide the pilot with unprecedented situational awareness and unmatched lethality and survivability.
Some of its salient features are :
- Dominates all adversaries in the air or on the surface.
- Has the ability to survive and prosecute the most formidable threats expected to emerge beyond 2020.
- Conducts air-to-air and air-to-ground combat missions simultaneously.
- Incorporates the most powerful and comprehensive sensor and mission avionics package ever to fly in a fighter.
Sukhoi’s T-50 PAK FA:

The Sukhoi PAK FA is a fifth-generation jet fighter being developed by Sukhoi for the Russian Air Force.The current prototype is Sukhoi’s T-50. The PAK FA, when fully developed, is intended to replace the MiG-29 Fulcrum and Su-27 Flanker in the Russian inventory and serve as the basis of the Sukhoi/HAL FGFA project being developed with India. As a fifth generation jet fighter, it is designed to directly compete with Lockheed Martin’s F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II. The T-50 performed its first flight January 29, 2010.Its second flight was on February 6 and its third on February 12. As of August 31, 2010, it made 17 flights in total.Sukhoi director Mikhail Pogosyan has projected a market for 1,000 aircraft over the next four decades, which will be produced in a joint venture with India, two hundred each for Russia and India and six hundred for other countries.He has also said that the Indian contribution would be in the form of joint work under the current agreement rather than as a joint venture. The Indian Air Force will “acquire 50 single-seater fighters of the Russian version” before the two seat FGFA is developed. The Russian Defense Ministry will purchase the first ten aircraft after 2012 and then 60 after 2016.
Medium Combat Aircraft (MCA):

The Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), formerly known as the Medium Combat Aircraft (MCA), is a twin-engined 5th generation stealth multirole fighter being developed by India. It will complement the HAL Tejas, the Sukhoi/HAL FGFA, the Sukhoi Su-30MKI and the yet undecided MRCA in the Indian Air Force. The main purpose of this aircraft is to replace the aging SEPECAT Jaguar & Dassault Mirage 2000. The Medium Combat Aircraft [MCA] is envisioned as a replacement for the British Jaguar and Mirage 2000 the IAF flies, which as of 2002 were to be phased out by 2015. Development costs were expected to be over US $2 billion. At that time, India’s DRDO intended to develop a stealth Medium Combat Aircraft, a further extension of its LCA design, in order to replace the Jaguar and Mirage inventory beginning around 2010.The MCA designers plan to pursue technologies superior to anything currently on offer. India’s aeronautical designers see the MCA programme as crucial for taking forward the expertise that has been painstakingly accumulated in the Tejas LCA programme.
J-XX Stealth Fighter:
China has already launched its next generation stealth fighter aircraft programme, and Shenyang Aircraft Industry Co. (SAC) has been selected to head research and development of a new fighter for the PLA Air Force (PLAAF). According to the reports, development of the subsystems including the engine and weapon suite for the next generation fighter, which was code named by the Western intelligence as J-XX, has been underway for some time. Images of the concepts show a twin-engine aircraft sharing some design traits with Lockheed Martin’s stealth F/A-22 “Raptor” multirole fighter such as the internal carriage of its weapons.
Not too much public information about the programme is available at the moment. Sources within China’s confirmed that the SAC is looking at a twin-engine, single-seat, single vertical tale fin design, but other design proposals has yet been ruled out. As China has developed close ties with Russia’s aerospace industry and has license produced many planes of formal Soviet designs, it can be predicted that the J-XX would include some, if not many Russian technologies and designs. China has been offered a ‘joint development and production’ of a new fifth-generation fighter by Russia -LFI. Russia has been trying to sell this concept both to China and India for some time, but neither of them has committed fully yet. Stealth and thrust vectoring are two must-have features in all aircraft being designed in the 21st century. It is not clear that how much progress Chinese designers have made in these areas, and Chinese aircraft industry may have to take Western/Israeli/Russian helps to make the J-XX truly fouth-generation (or fifth-generation using the Russian standards). Once introduced, the J-12′s immediate rival will be U.S. F/A-22, JSF and India’s MCA (Medium Combat Aircraft).
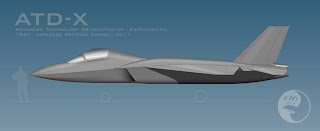
JASDF Stealth Fighter ATD-X:
JASDF (Japan Air Self-Defense Forces) planners have been attempting to acquire the American F-22 Raptor jet fighter to replace their current F-15 Eagle fighter planes. The F-22 Raptor is packed with the latest avionics and stealth technology but its high tech features have the Pentagon concerned about security leaks. Even though the United States would lose out financially by not selling Japan the F-22, security issues are front & center these days and Japan is now looking to its own aircraft designers to provide a home-grown solution.

The Mitsubishi ATD-X Shinshin is a Japanese aircraft being developed by the Ministry of Defense Technical Research and Development Institute (TRDI) for research purposes. ATD-X is an acronym which represents “Advanced Technology Demonstrator – X”. The main contractor is Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. This aircraft will be used as a technology demonstrator and research prototype to determine whether domestic advanced technologies for a fifth generation fighter aircraft are viable. The aircraft’s first flight is scheduled for 2014. The design of the aircraft reflects those of several American fourth and fifth generation fighters, most notably the F-22. Japan is set to develop its own next-generation stealth fighter jets to reduce its dependence on foreign technology and counter similar moves by China and Russia.